Aviation

ME1037
B-52 Stratofortress™
3.25 Sheets
Challenging
The B-52 Stratofortress™ is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. It was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. The B-52 has been a mainstay of the United States Air Force since 1955 and is expected to remain in service through 2050. The bomber can carry up to 70,000 pounds of weapons and has a combat range of around 8,800 miles.
$0.00
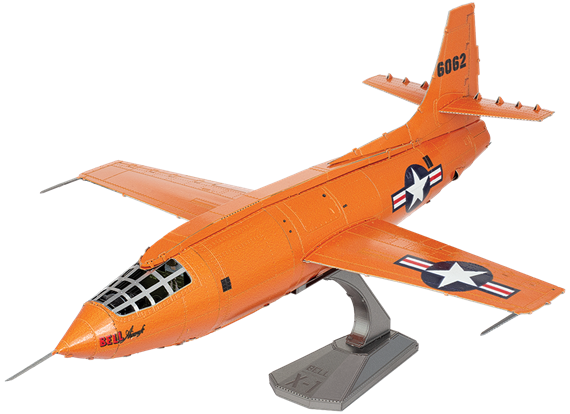

ME1039
Bell® X-1
3 Sheets
Moderate
On 14 October 1947, the Bell X-1 rocket powered experimental aircraft, piloted by the legendary test pilot, Chuck Yeager, became the first airplane to fly faster than the speed of sound. To accomplish this feat, the aircraft was air-launched at 7,000 meters (23,000 feet) from the belly of a WWII bomber. In tribute to his wife, Yeager named the airplane "Glamorous Glennis".
$0.00
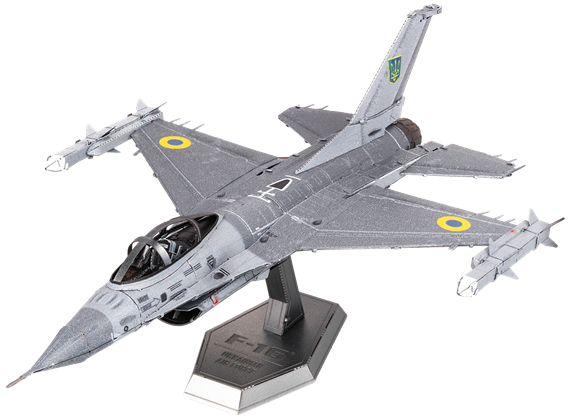

ME1046U
F-16 Fighting Falcon® Ukrainian Air Force
3 Sheets
Moderate
The F-16 Fighting Falcon® is a light weight, single engine fighter jet capable of flying at twice the speed of sound. It was first produced by General Dynamics™, Lockheed Martin® and various licensed manufacturers. It is the most common fixed-wing aircraft in military service today and has been used by the air forces of more than 25 countries.
$0.00

ME1040
MiG-15
3 Sheets
Moderate
The MiG-15 is a single-seat, single-engine Soviet jet fighter, built by the Russian aerospace and defense company, Mikoyan-Gurevich (MiG). It was used extensively in combat during the Korean War (1950–53). When first introduced into the Korean war, the United States was shocked by the plane’s speed, climbing ability, and high operating ceiling. In response, the United States hurried to deliver the new F-86 Sabre jet in order to reestablish U.S. air supremacy in the war.
$0.00
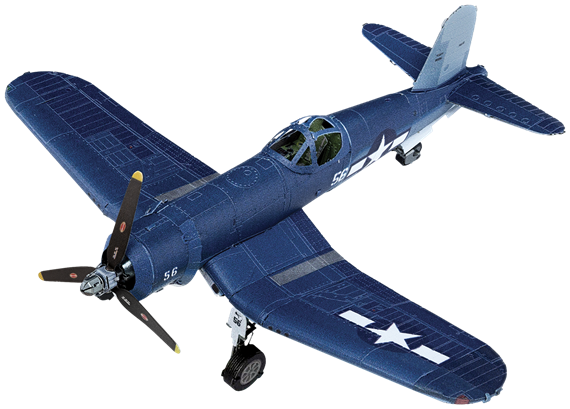

ME1030
F4U Corsair™
2 Sheets
Challenging
The most capable carrier based fighter-bomber of World War II featured the largest engine available at the time: the 2,000 hp, 18-cylinder Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp radial. It was the first US warplane to exceed 400 mph in level flight. The plane featured an unusual inverted gull wing to keep the undercarriage short while allowing the use of the large diameter propeller demanded by the powerful engine.
$0.00
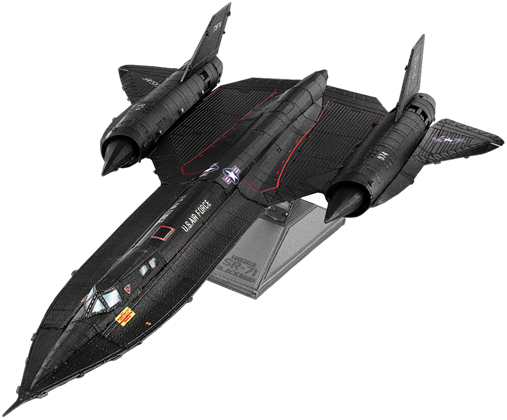

ME1034
Lockheed® SR-71® Blackbird®
2.5 Sheets
Moderate
Was a long-range, Mach 3.5+ strategic reconnaissance aircraft developed by Lockheed and its Skunk Works® division. It was the first aircraft to be constructed mainly of titanium. At full velocity the airplane surface heats up to over 260°C+ (500 °F). A total of 3,551 missions were flown and not one Blackbird was lost due to enemy military retaliation.
Note: Skunk Works is the nickname for Lockheed's Advanced Development Programs. Skunk Works engineers have developed highly advanced, military aircraft, often in secret, since World War II.
Note: Skunk Works is the nickname for Lockheed's Advanced Development Programs. Skunk Works engineers have developed highly advanced, military aircraft, often in secret, since World War II.
$0.00

ME1025
Lockheed Vega 5B
2 Sheets
Moderate
This Lockheed Vega 5B monoplane was purchased in 1932 by the famous aviator, Amelia Earhart, who called it her “Little Red Bus”. The plane was powered by a 450 hp engine with a cruise speed of 155 mph. Flying this plane in 1932, Amelia became the first woman to fly nonstop across the Atlantic Ocean, and to make a solo nonstop flight across the United States.
$0.00

ME1024
SPAD S.XIII
2 Sheets
Moderate
The SPAD S.XIII was a World War I French single-seat biplane fighter aircraft that proved to be one of the most capable fighters of the war, as well as one of the most-produced, with 8,472 built. Many celebrated WWI pilots flew the SPAD XIII including America's highest scoring ace, Captain Eddie Rickenbacker.
$0.00

ME1023
Sopwith Camel
2 Sheets
Moderate
The Sopwith Camel is a British World War I single-seat biplane fighter aircraft introduced on the Western Front in 1917. Unmatched in its maneuverability, it achieved more aerial victories than any other allied aircraft during the war. Also, the legendary WWI ace, Snoopy, flew this plane in his many dog fights against The Red Baron.
$0.00
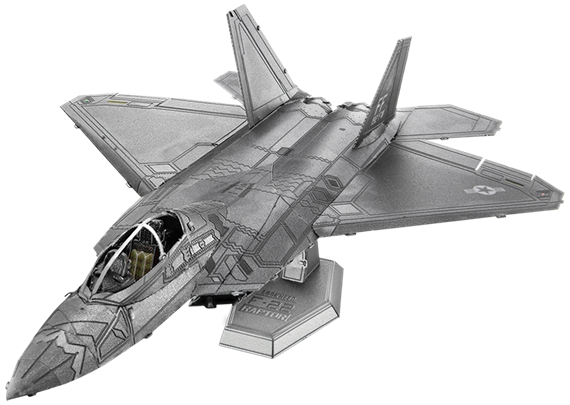

ME1016
F-22® Raptor®
3 Sheets
Moderate
The Lockheed Martin F-22® Raptor® is a single-seat twin-engine fifth-generation super-maneuverable fighter aircraft that uses stealth, speed, agility, precision and situational awareness, combined with air-to-air and air-to-ground combat capabilities, makes it the best overall fighter in the world today.
$0.00

ME1015
F-86 Sabre
3 Sheets
Moderate
The F-86 Sabre is a United States transonic jet fighter, first deployed during the Korean War. As the first US swept-wing fighter, the F-86 Sabre was engineered to counter the Soviet MiG-15. Produced by North American Aviation, the F-86 was considered one of the most important combat aircraft during the early 1950s.
$0.00

ME1013
Consolidated PBY Catalina
3 Sheets
Moderate
The PBY Catalina was one of the most widely flown amphibious aircraft during WWII. During the war, it was used in anti-submarine warfare and as a long-range patrol bomber, a convoy escort, and a cargo transport. Our model is based on the airworthy Catalina, Miss Pick Up, which is located in the Imperial War Museum at Duxford, UK. It represents a U.S. Army Air Forces aircraft lost to enemy action in Europe at the end of March 1945.
To learn more about her, go to catalina.org.uk
To learn more about her, go to catalina.org.uk
$0.00

ME1012
Mitsubishi Zero
2 Sheets
Moderate
The Mitsubishi Zero was considered to be the most capable carrier-based fighter aircraft in the world when it first entered combat in 1940. Its superior capabilities were in part due to its amazingly light weight that made it one of the fastest, most maneuverable and one of the longest-ranged single-engine fighter aircraft of World War II. However, that tradeoff in weight was at the price of not having self-sealing fuel tanks which made it prone to catching fire and exploding when struck by enemy fire, and no armor protection for either the pilot or the engine.
$0.00

PS2011
The Spruce Goose
3 Sheets
Moderate
The Hughes H-4 Hercules nicknamed the Spruce Goose by critics, was designed as a transatlantic transport plane for use during World War II though it was not completed until after the war. Due to restrictions during the war on the use of aluminum and also concerns about weight, the plane was built almost entirely of birch wood. It was the largest amphibious plane to ever fly though that was only one brief flight on November 2, 1947. The aircraft remains in good condition and is currently on display at the Evergreen Aviation & Space Museum in McMinnville, Oregon, USA.
$0.00
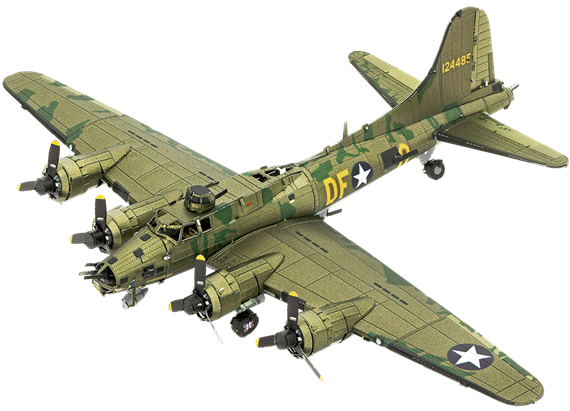

ME1009
B-17 Flying Fortress™
2.5 Sheets
Challenging
B-17 Flying Fortress was a World War II heavy bomber. Its turbo-supercharged radial engines gave it the necessary high-altitude performance to fly above the effective range of antiaircraft artillery.
$0.00
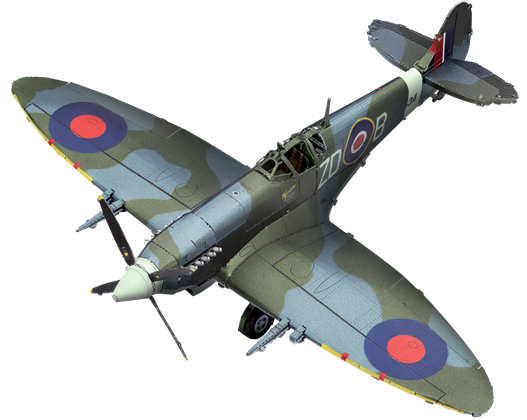
ME1005
Supermarine Spitfire
2 Sheets
Moderate
The most widely produced and strategically important British single-seat fighter of World War II. The Spitfire, renowned for winning victory laurels in the Battle of Britain (1940-41), served in every theatre of the war and was produced in more variants than any other British aircraft.
$0.00